Why and When do you need this Model
A generic framework for Change Management derived by summarising research into best practice. Consistent with but independent of any specific Change Management methodology. Use to design change leadership curricula, key skills and assessments outside of specific methodologies.
The Bare Essentials
The 12 core principles are:
- What’s the Story of the Change?
- Have a Change Plan
- Never fly blind
- Measure twice - cut once
- Round up your supporters
- But don’t ignore powerful opponents
- Influence the Influential
- If you can’t be direct, then be indirect
- Don’t forget those you helped get you started
- Rome was not built in a day
- Expect unexpected Change
- Finally, rip up that Change cookbook
Figure A

Why and When do you need this Model
A Change Narrative is a concise explanation of why a major change is necessary at this point it time. Once developed it needs to be communicated to colleagues at all levels. (See also “Lift Conversation” and “Objection Handling”).
The Bare Essentials
- Why do we need to change?
- What is the main reason for the change ("burning platform" or "golden opportunity")?
- Why do we need to change now when we did not need to change before?
- Why can’t we defer this change until next year?
- Who decided that we need to change anyway?
- What is the hard measurable evidence to justify this change?
- Do all our leaders believe this change is essential? What do they say?
- Have we fully considered the consequences of not changing?
- Has anyone else successfully made this type of change?
- What is the business case for the change?
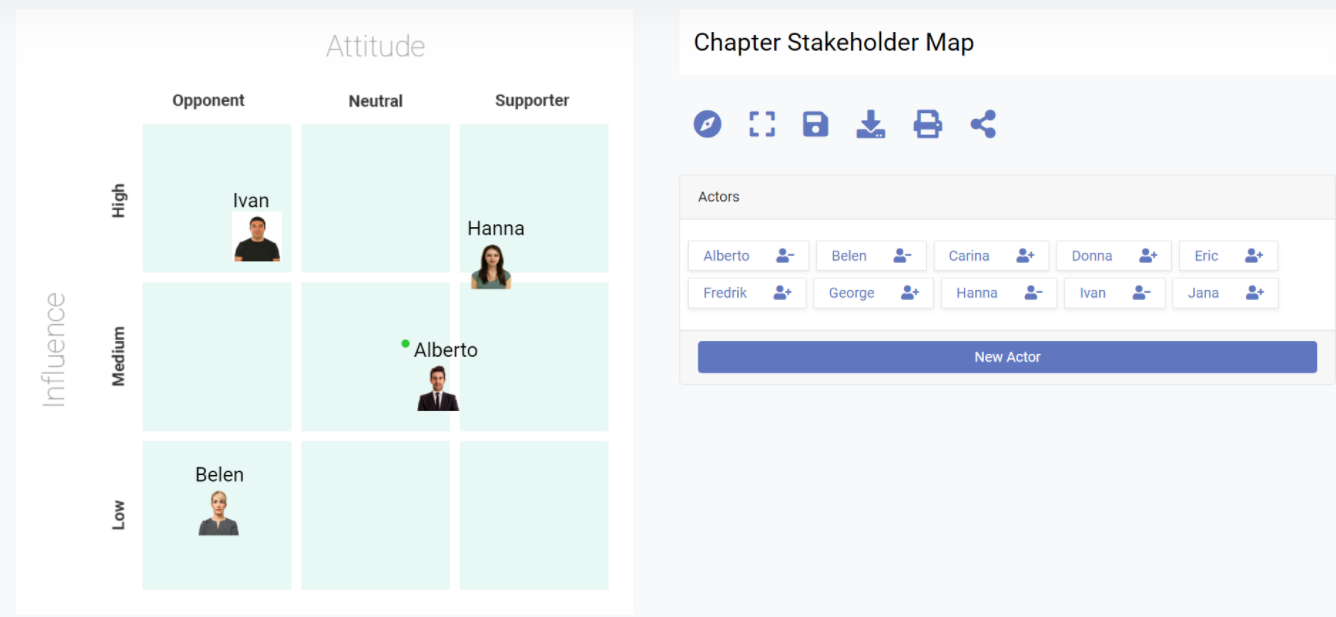
Why and When do you need this Model
Stakeholder Mapping is a technique which should be used at the beginning of major programmes involving any kind of significant change to establish which stakeholders need to be engaged first.
The Bare Essentials
Stakeholder Mapping allows you to construct a simple 3x3 matrix showing Influence (Organizational or Social) on one axis and the Stakeholder’s Attitude (Supporter, Neutral or Opponent) on the other axis.
Organisational Influence is power due to a person’s formal authority, such as their position in an Organisation.
Social Influence is power due to a person’s informal authority and is usually a combination of their reputation and the extent of their social network.
In terms of assessing Attitude you are looking for the person’s attitude to the proposed change NOT to you personally.
Figure B
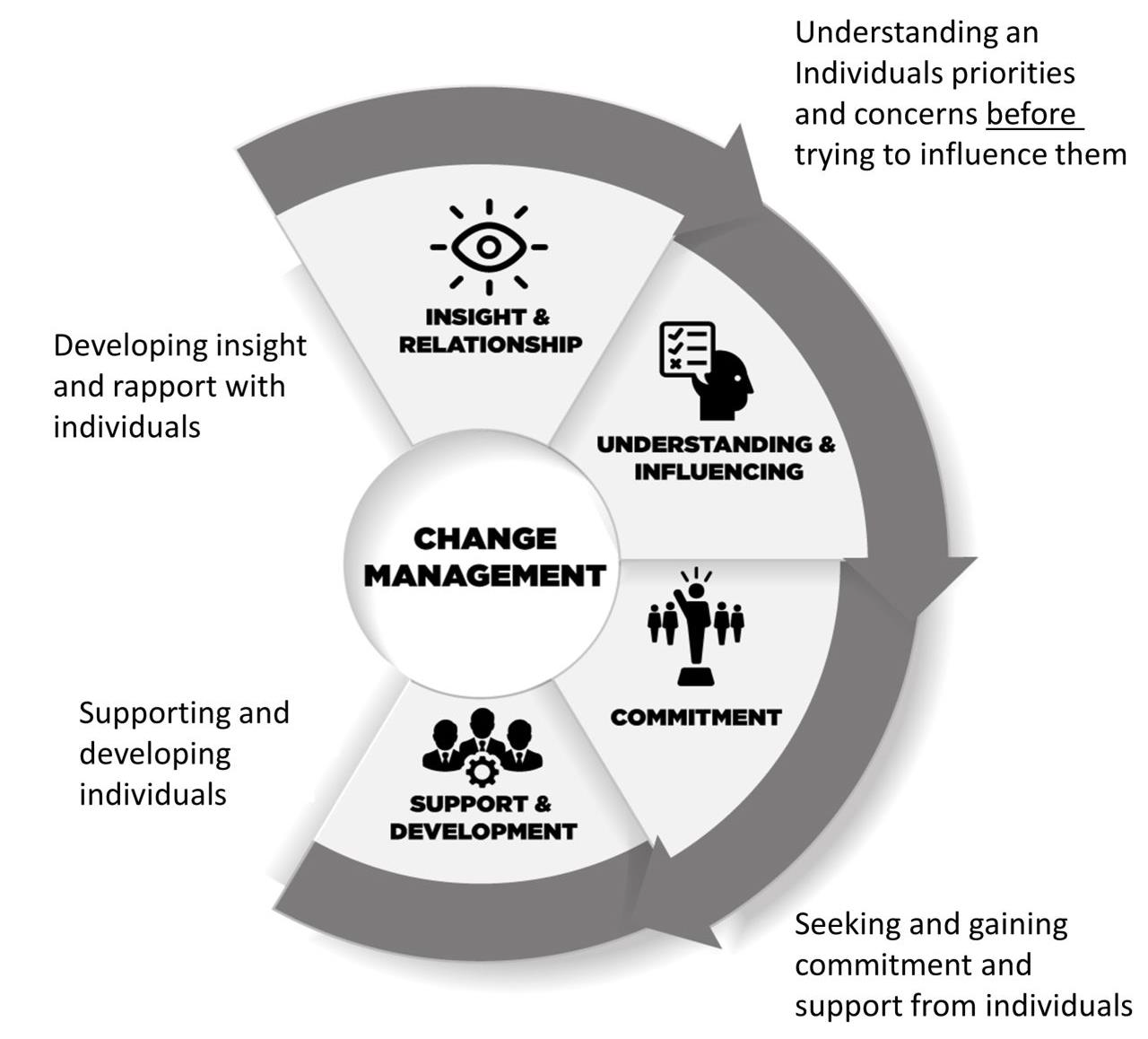
Why and When do you need this Model
The Change Engagement Tool provides a guide for the types of conversations you will need to influence someone for a proposed change.
The Bare Essentials
There are 4 aspects which are fundamental to being able to influence anyone for change:
- Insight and Relationship
- Understanding and Influencing
- Gaining Commitment
- Support and Development
These four aspects have an implied sequence 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4 and reflect 4 key Change Management principles:
- Build rapport and relationship before you have serious conversations with people.
- Explore what people feel and want before you ask a person to commit to anything.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for support when/if the groundwork has been done and the conditions are right.
- Provide on-going support to anyone who has made a commitment to you don’t just forget about them!
Figure C
Why and When do you need this Model
It’s easy to get lost in change theories, models, principles and tools the 4H model brings you right back to the essentials.
The Bare Essentials
-
Head
Is there a compelling reason for the change succinctly articulated? By NOT changing you must be exposing your organization to a major threat or walking away from a major opportunity (even better, both).
-
Heart
Heart is the "appetite" for change in the sponsors. So many change initiatives with great HEAD flounder because the senior leaders did not want it badly enough or thought that the compelling reason was somehow sufficient in itself.
-
Hands
Next you need the HANDS the detailed agreed change plan with deadlines, deliverables, new processes, systems, incentives, practices, success measures and key behavior changes.
-
Heels
Finally you need the HEELS on the ground to deliver the change. I have never yet seen a change successfully delivered without a motivated and competent project manager working to a public and serious deadline.
Figure D

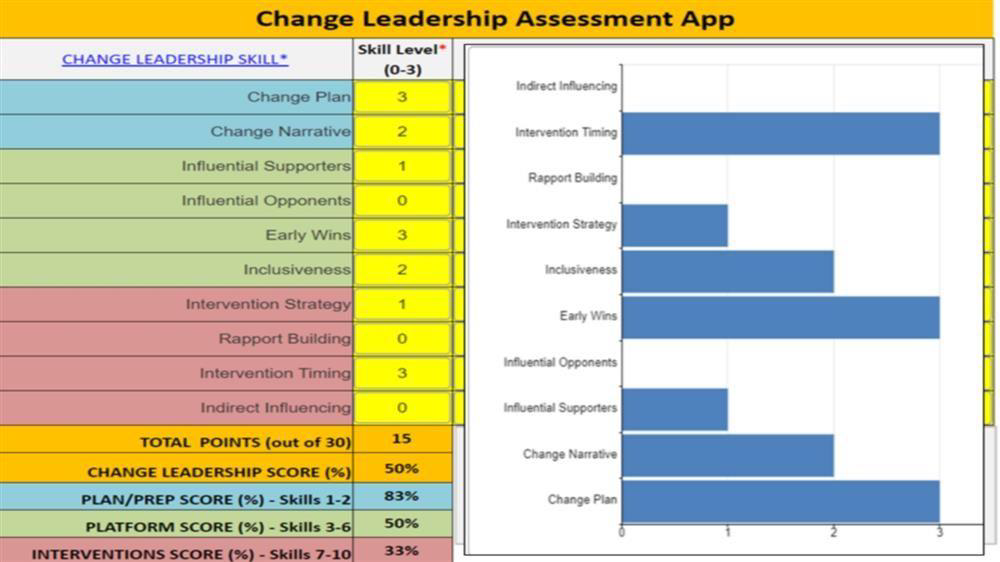
Why and When do you need this Model
This model identifies 10 practical skills you need to be an effective change leader.You can use the app to assess yourself and your colleagues.
The Bare Essentials
The 8 key change leadership skills can be summarised as follows:
A. Change Planning
- Developing, following and adjusting a well researched change plan.
- Developing and communicating a compelling change narrative.
B. Change Platform
- Building around influential supporters.
- Engaging influential opponents early.
- Getting early wins (change champions).
- Broadening change platform when required (and not neglecting people).
C. Change Interventions
- Evidence of an intervention strategy.
- Building rapport where necessary first before making other interventions.
- The right intervention at the right time.
- Making use of both direct and indirect interventions.
Figure E
Why and When do you need this Model
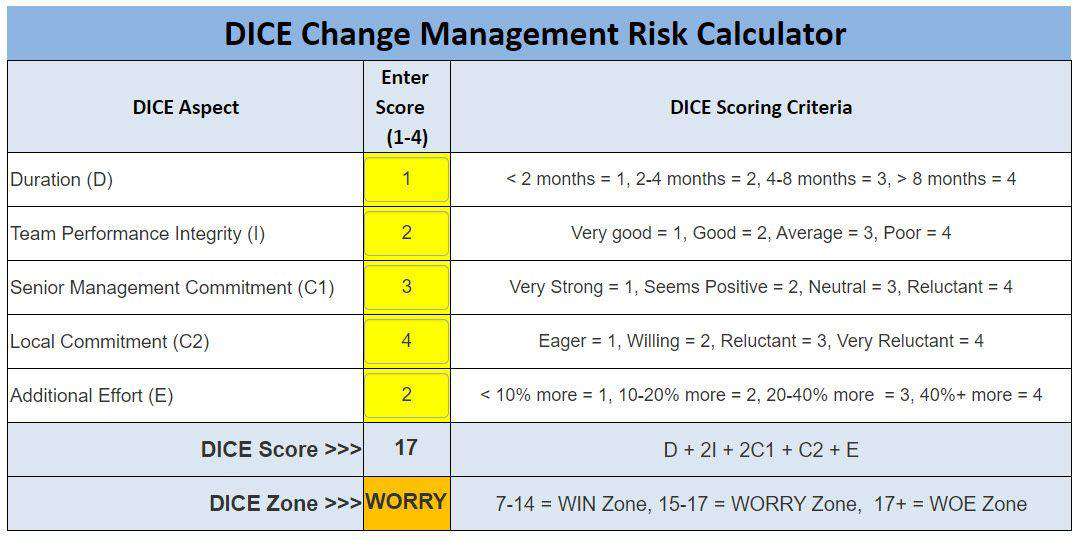
The DICE Tool, originally developed by the Boston Consulting Group based on research into more than 200 major change initiatives, enables a quick risk assessment of any proposed Change Programme/Initiative.
The Bare Essentials
The DICE model allows you to quickly place proposed Change Programmes into one of three risk bands:
- WIN (Low Risk) DICE; Score 7 - 14
- WORRY (Medium Risk) DICE; Score 15 - 17
- WOE (High Risk) DICE; Score 17+
To score a project for DICE you simply rank the project on the 5 aspects below, each on a scale of 1 - 4 (the higher the number the higher the risk associated with the aspect):
- Project Duration
- Team Integrity
- Sponsor Commitment
- Local Management Commitment
- Additional Effort required
Figure F
Why and When do you need this Model
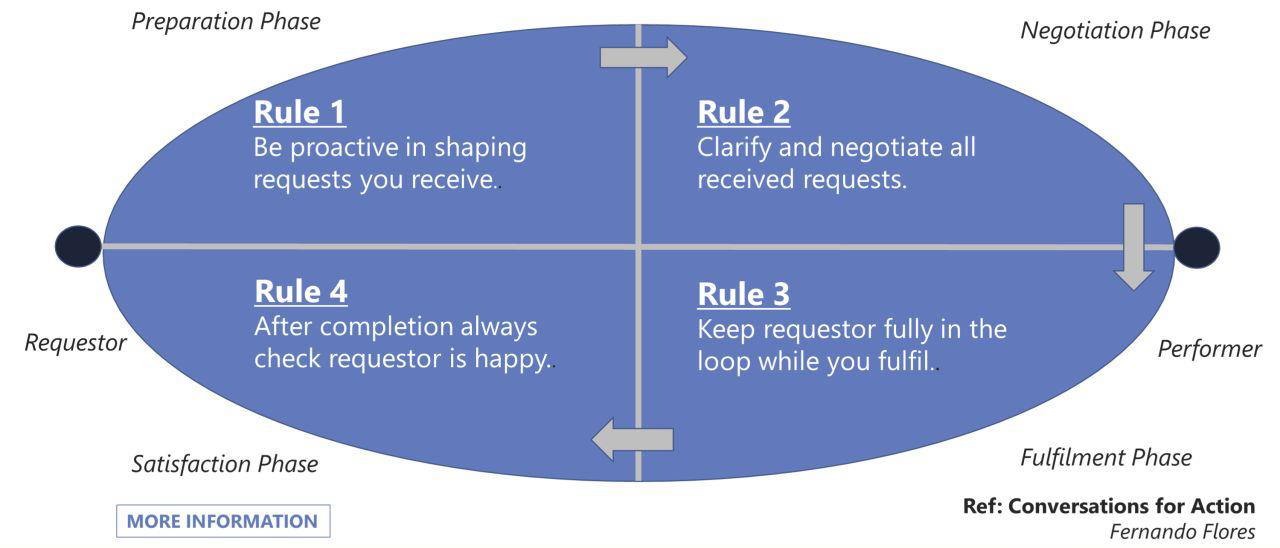
This model (aka Commitment based Management) helps manage conversations and commitments with any Stakeholder.
The Bare Essentials
Warning: CbM is a rich body of work developed over the last 50 years we are only scraping the surface here.
-
Be proactive in shaping requests you receive
Don’t wait for requests to come in. Much better to anticipate them and make “Offers”. You will show up as a much more powerful partner!
-
Clarify and negotiate all received requests
Never accept a request (verbal or written) without clarifying and if necessary negotiating what you are being asked to achieve (“Conditions of satisfaction”).
-
Keep requestor fully in the loop while you fulfil
Keep requestor informed about how the job is going particularly when there are complications as you may need to revert to Rule 2.
-
After completion always check requestor is happy
It’s not done when you think Its done! It’s done when the requestor declares satisfaction with what you have done. Also apply Rule 1!
Figure G
Why and When do you need this Model
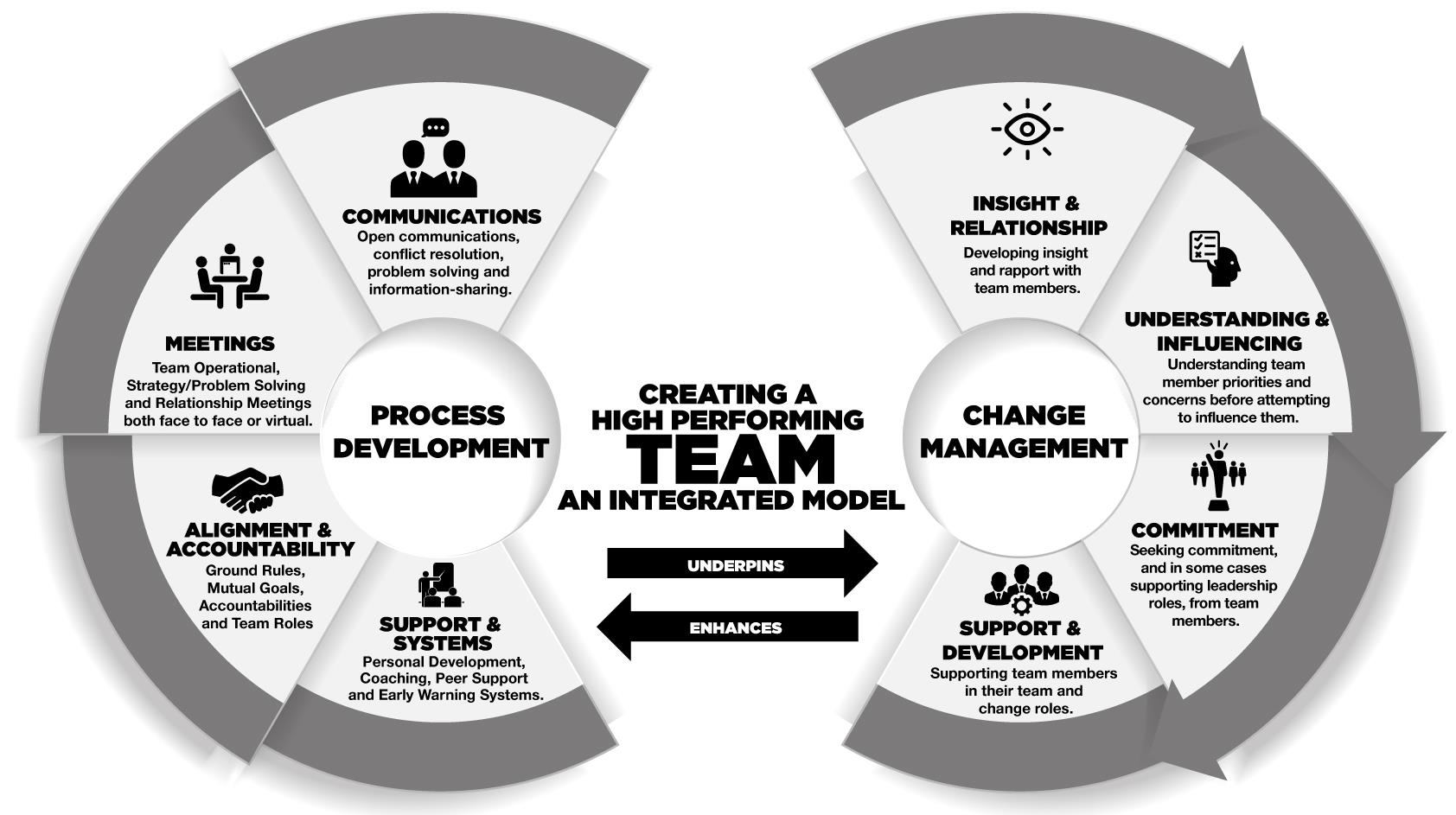
The Racetrack Tool is a way to bring change into a team you lead based on the premise creating a team requires both Change Management and Process Development.
The Bare Essentials
Unlike the more common Stakeholder Change, in Team Change you have direct authority over the colleagues on your team however you may face other challenges including engaging with those who feel they, not you, should be the leader of the team. Also, dealing with more operational colleagues who may lack the communications skills and big picture perspective which senior stakeholders should possess.
The Racetrack Tool suggests you address the unique change issues of each team member:
- Insight & Relationships
- Understanding & Influencing
- Commitment
- Support & Development
Whilst also addressing the process fundamentals of the whole team:
- Communications
- Meetings
- Alignment & Accountability
- Support & Systems
Figure H
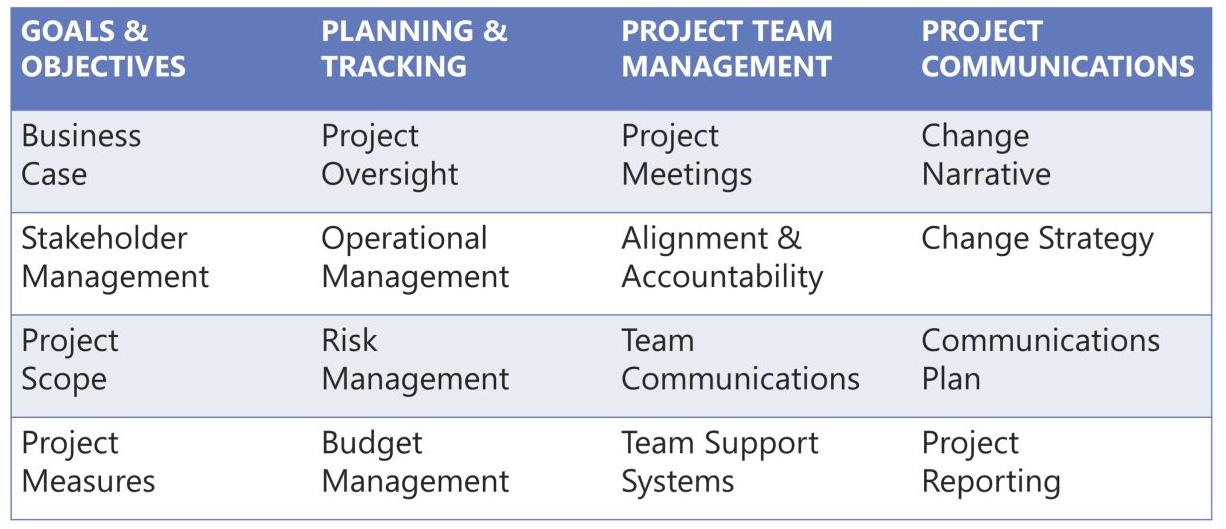
Why and When do you need this Model
This document provides a comprehensive breakdown of the key aspects which need to be addressed in the planning of any major Change Initiative.
The Bare Essentials
-
Goals & Objectives
- Business Case
- Stakeholder Management
- Project Scope
- Project Measures
-
Planning & Tracking
-
Project Team Management
- Project Meetings
- Alignment & Accountability
- Team Communications
- Team Support Systems
-
Project Communications
- Change Narrative
- Change Strategy
- Communications Plan
- Project Reporting
Figure I